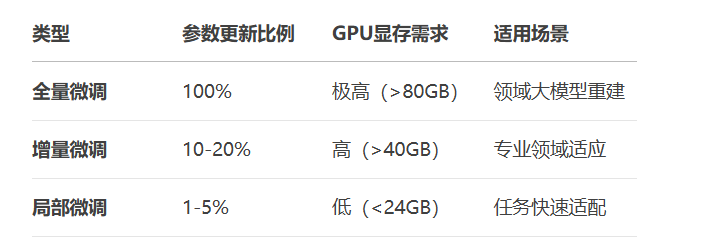
数学表达:
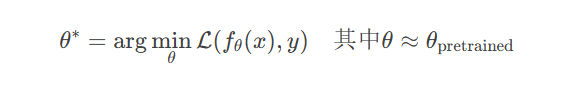

参数高效微调公式:
其中 $B \in \mathbb{R}^{d \times r}$, $A \in \mathbb{R}^{r \times k}$, $r \ll \min(d,k)$
代码实现:
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model lora_config = LoraConfig( r=8, lora_alpha=32, target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"], lora_dropout=0.05 ) model = get_peft_model(base_model, lora_config)
高质量数据格式:
{
"instruction": "解释量子纠缠现象",
"input": "",
"output": "量子纠缠是量子力学中的现象...",
"system": "你是一位量子物理教授"
}数据生成策略:
# 使用大模型生成合成数据
def generate_instruction_data(prompt_template, num_samples):
results = []
for _ in range(num_samples):
prompt = prompt_template.format(subject=random.choice(SUBJECTS))
response = llm.generate(prompt, max_length=200)
results.append({"instruction": prompt, "output": response})
return results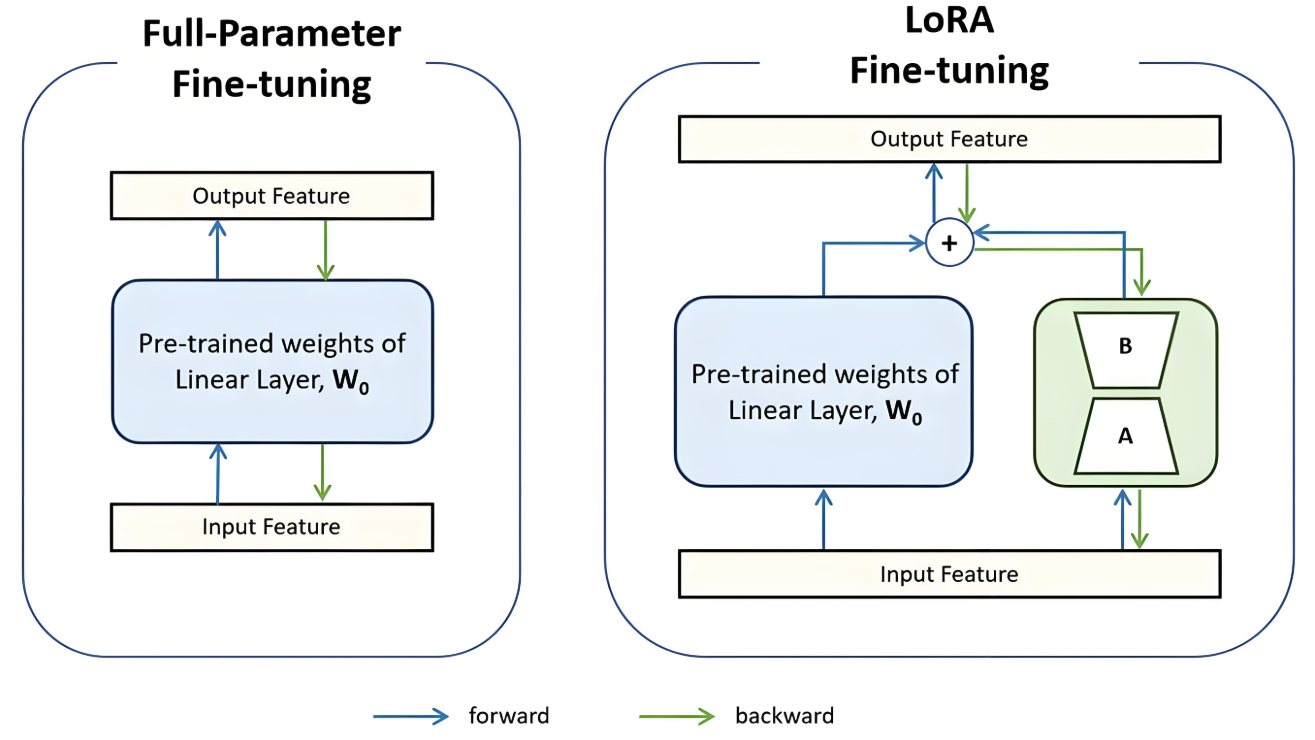
矩阵近似公式:
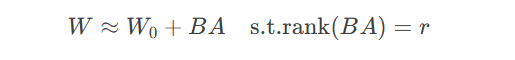
其中 $W_0$ 冻结,$B$ 和 $A$ 可训练
内存优化对比:
# 原始参数量
full_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
# LoRA参数量
lora_params = 0
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if "lora" in name:
lora_params += sum(p.numel() for p in module.parameters())
print(f"全量微调参数: {full_params/1e6:.1f}M")
print(f"LoRA参数: {lora_params/1e3:.1f}K")from peft import PeftModel
# 加载基础模型
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("llama-7b")
# 添加不同领域的LoRA适配器
medical_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, "medical_lora")
legal_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, "legal_lora")
# 运行时切换
def switch_adapter(model, adapter_name):
model.set_adapter(adapter_name)
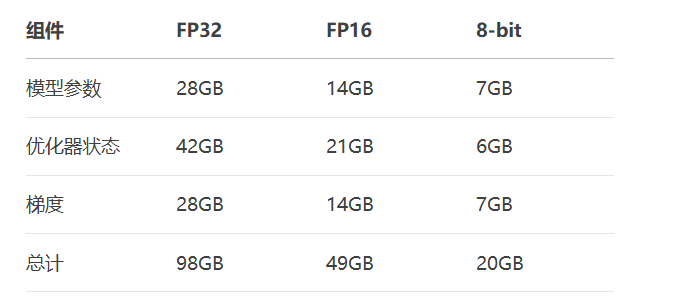
model.eval()显存组成公式:
计算示例(7B模型):
QLoRA配置:
from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig( load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4", bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16 ) model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained( "llama-7b", quantization_config=bnb_config, device_map="auto" )
梯度裁剪:
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
损失缩放(FP16训练):
scaler = GradScaler() with autocast(): outputs = model(inputs) loss = outputs.loss scaler.scale(loss).backward() scaler.step(optimizer) scaler.update()
# 转换HuggingFace模型到GGUF格式 python convert.py models/llama-7b --outtype f16 quantize models/llama-7b-f16.bin models/llama-7b-Q5_K.gguf Q5_K
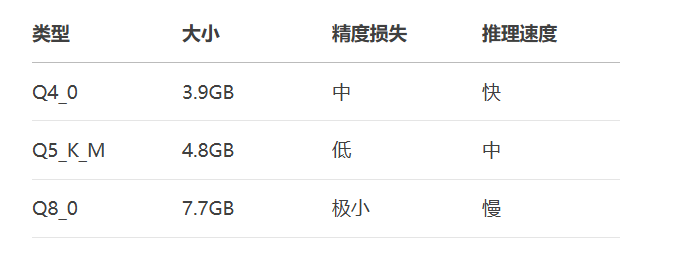
量化类型对比:
5.2 vLLM部署配置
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams llm = LLM(model="llama-7b-Q5_K.gguf", quantization="gguf") sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.8, max_tokens=200) outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params) for output in outputs: print(output.outputs[0].text)
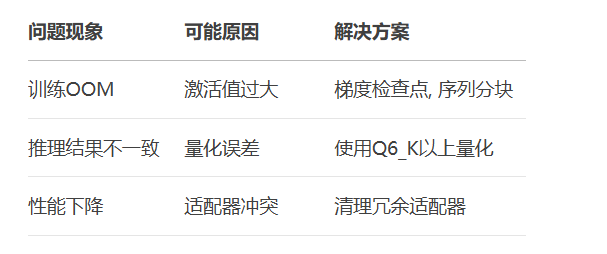
问题根源:
量化误差累积
算子实现差异
推理框架优化策略不同
解决流程:
graph LR A[训练框架] --> B[FP32模型] B --> C[GGUF转换] C --> D[部署框架] D --> E[一致性校验] E -->|失败| F[误差分析] F --> G[调整量化参数] G --> C
# 使用DeepSpeed Zero-3
deepspeed_config = {
"train_batch_size": 32,
"gradient_accumulation_steps": 2,
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_param": {
"device": "cpu"
}
},
"bf16": {
"enabled": True
}
}
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
data_collator=collator,
deepspeed=deepspeed_config
)# 使用Prometheus+Grafana监控
from prometheus_client import start_http_server, Gauge
vram_gauge = Gauge('gpu_vram', 'GPU VRAM usage')
latency_gauge = Gauge('inference_latency', 'Inference latency')
def monitor():
while True:
vram = get_gpu_vram()
latency = get_inference_latency()
vram_gauge.set(vram)
latency_gauge.set(latency)
time.sleep(5)class ContinuousFinetuning:
def __init__(self, base_model):
self.model = base_model
self.data_buffer = []
def add_feedback(self, user_input, model_output, rating):
self.data_buffer.append({
"input": user_input,
"output": model_output,
"rating": rating
})
if len(self.data_buffer) > 1000:
self.retrain()
def retrain(self):
dataset = self.create_dataset(self.data_buffer)
trainer = Trainer(
model=self.model,
train_dataset=dataset,
args=TrainingArguments(per_device_train_batch_size=4)
)
trainer.train()
self.data_buffer = []graph TD A[基础模型] --> B[高效微调] B --> C[量化压缩] C --> D[高速推理] D --> E[持续优化]
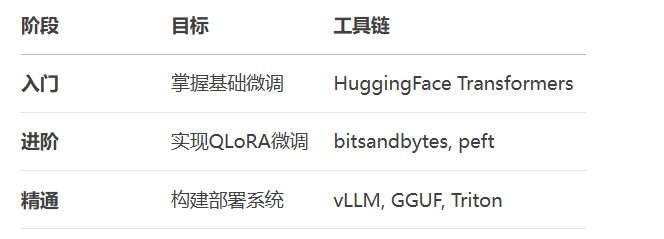
更多AI大模型应用开发学习内容视频和资料,尽在聚客AI学院。